A vibrant tapestry of ancient traditions and cutting-edge innovation, India stands at a critical juncture in its journey towards becoming a global leader. Embedded within this vision lies “2030 Ka Bharat” – a transformative roadmap guided by the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). Adopted by 193 countries in 2015, these 17 ambitious goals present a blueprint for a sustainable and equitable future, encompassing everything from ending poverty and hunger to ensuring quality education and combating climate change.
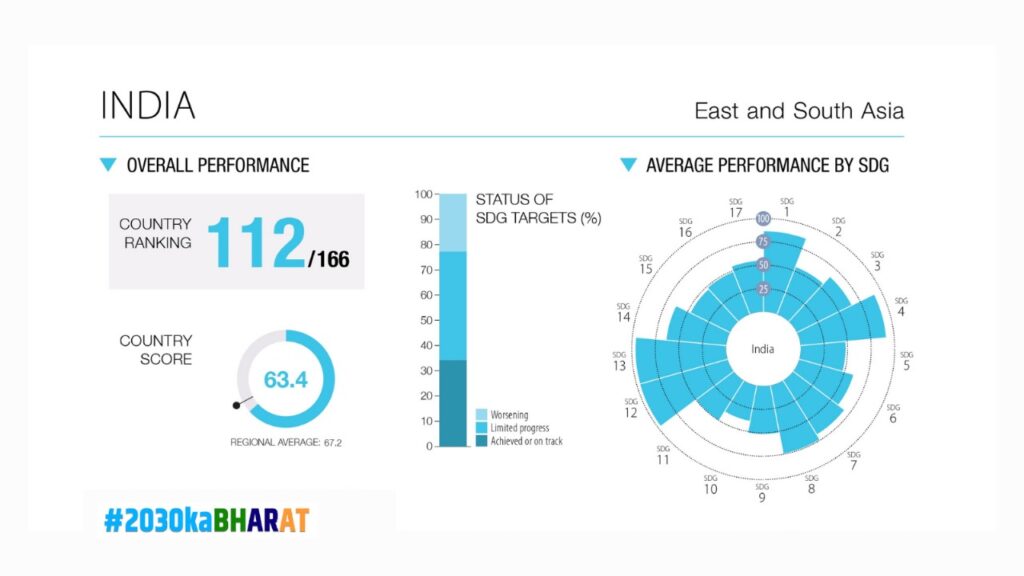
India’s commitment to the SDGs is unwavering. The country ranked 112nd in the 2023 SDG Index, with significant progress in several areas. The 2022 World Investment Report by UNCTAD recognizes India’s ambitious national plans for achieving the SDGs, such as the Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana for financial inclusion and the Swachh Bharat Abhiyan for sanitation. However, challenges remain, and accelerating progress demands both collective effort and strategic action.
Building a Future Free from Poverty and Hunger:
Ending poverty (SDG 1) and hunger (SDG 2) remains a crucial priority. In 2021, 23% of Indians lived below the national poverty line (World Bank, 2023). Initiatives like the Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana, providing affordable housing, and MGNREGA, guaranteeing rural employment, offer crucial support. While India achieved the MDG for hunger reduction in 2015, persistent malnutrition highlights the need for further investment in agricultural productivity, dietary diversification, and social safety nets.
Ensuring Good Health and Quality Education:
India has made remarkable strides in healthcare (SDG 3), with Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana expanding health insurance coverage. Maternal mortality rates have declined significantly, while life expectancy has risen to 68 years (World Bank, 2023). However, challenges persist in rural areas, and strengthening primary healthcare and addressing malnutrition are crucial priorities.
Quality education (SDG 4) forms the bedrock of a brighter future. India’s Right to Education Act has boosted enrollment rates, and the Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan program prioritizes universal access to elementary education. Yet, bridging the quality gap between rural and urban schools and promoting vocational and skill development remain critical tasks.
Empowering Women and Promoting Gender Equality:
Despite progress, gender inequality (SDG 5) persists in India. Initiatives like Beti Bachao Beti Padhao strive for girl child education and women’s empowerment. The Sexual Harassment of Women at Workplace Act and efforts to combat domestic violence offer necessary protections. However, tackling entrenched societal biases and ensuring greater economic participation for women remain long-term challenges.
Investing in Clean Water, Sanitation, and Sustainable Energy:
Securing access to clean water and sanitation (SDG 6) is essential for public health and well-being. Swachh Bharat Abhiyan has significantly improved sanitation coverage, but challenges remain in rural areas and wastewater management. Providing safe drinking water, particularly in marginalized communities, requires continued investment and infrastructure development.
India’s ambitious renewable energy targets align with SDG 7 for affordable and clean energy. The National Solar Mission and increasing wind power capacity showcase India’s commitment to clean energy transition. However, achieving energy efficiency in industries and reducing fossil fuel dependence require sustained efforts.
Creating Decent Work and Fostering Sustainable Growth:
India’s young and growing population necessitates strong focus on decent work and economic growth (SDG 8). Skill development programs like Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana equip individuals for better employment opportunities. Initiatives like Make in India aim to boost manufacturing and generate jobs. However, bridging the urban-rural employment gap and promoting inclusive growth for all remain critical challenges.
Building Sustainable Cities and Responsible Consumption:
India’s rapid urbanization necessitates developing sustainable cities and communities (SDG 11). Smart city initiatives promote efficient infrastructure and green spaces. However, managing waste effectively and addressing air pollution require urgent attention. Additionally, promoting responsible consumption patterns (SDG 12) through awareness campaigns and eco-friendly product choices is crucial to ensuring long-term sustainability.
Combating Climate Change and Protecting Ecosystems:
The urgent need to combat climate change (SDG 13) is evident in India’s increasing vulnerability to extreme weather events. India’s Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs) under the Paris Agreement outline ambitious renewable energy targets and adaptation strategies. Protecting marine ecosystems (SDG 14) and biodiversity on land (SDG 15) also require continued efforts. Marine conservation initiatives and the Green India Mission for afforestation showcase India’s commitment to environmental protection.
Strengthening Institutions and Fostering Partnerships:
Achieving the SDGs demands strong institutions and effective governance (SDG 16). Anti-corruption initiatives and reforms in the judicial system promote transparency and accountability. Partnerships for the Goals Collective Action for an Equitable Future
Partnerships for the Goals (SDG 17) lie at the heart of India’s 2030 Ka Bharat vision. The government actively collaborates with civil society organizations, private sector entities, and international partners like the UN and development agencies. Initiatives like the SDG India Index & Dashboard and the SDG Knowledge Hub facilitate data sharing, best practices exchange, and multi-stakeholder engagement.

Challenges and Opportunities: Navigating the Road Ahead
While India has made notable progress towards the SDGs, several challenges remain. Poverty and inequality persist, particularly in rural areas. Inadequate healthcare infrastructure, limited access to quality education, and gender discrimination hinder progress on multiple fronts. Environmental degradation, exacerbated by climate change, poses a significant threat to sustainable development.
Despite these challenges, India possesses diverse strengths and vibrant opportunities. Its young and increasingly skilled population presents a demographic dividend that can be harnessed for economic growth and innovation. Technological advancements offer solutions for improving healthcare, education, and environmental monitoring. Rising public awareness and growing engagement from civil society create a fertile ground for collective action.
Accelerating Progress: Charting the Course for 2030 Ka Bharat
To expedite progress towards 2030 Ka Bharat, India needs to:
- Enhance data collection and analysis: Accurate and disaggregated data are crucial for identifying disparities and prioritizing interventions effectively.
- Strengthen public-private partnerships: Leveraging private sector expertise and resources can bridge funding gaps and accelerate infrastructure development.
- Empower local communities: Bottom-up approaches that engage local communities in decision-making processes lead to more sustainable and inclusive development outcomes.
- Embrace technological innovation: Utilizing technologies like artificial intelligence, blockchain, and remote sensing can revolutionize service delivery and address development challenges.
- Promote financial inclusion: Expanding access to financial services, particularly for women and marginalized communities, empowers individuals and fosters economic growth.
- Invest in renewable energy and clean technologies: Transitioning to a low-carbon economy not only combats climate change but also creates new jobs and fosters sustainability.
- Strengthen environmental protection: Prioritizing forest conservation, biodiversity protection, and pollution control are essential for a healthy planet and future generations.
Conclusion: A Future We Can Build Together
2030 Ka Bharat is not just a vision; it is a call to action. The journey towards achieving the SDGs demands collective effort, unwavering commitment, and innovative solutions. From government leaders and corporations to civil society organizations and individual citizens, everyone has a role to play. By embracing collaboration, harnessing technology, and fostering a spirit of inclusivity, India can transform its aspirations into reality, leading the way towards a more just, equitable, and sustainable future for all.
Resources:
Sustainable Development Report – https://dashboards.sdgindex.org/chapters
