The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) represent a global commitment to address pressing challenges and build a sustainable future. At the heart of this collective effort lies the concept of “Partnership for the Goals,” emphasizing collaboration among governments, the private sector, and civil society. In the context of India, a country marked by diversity and complexity, understanding the nuances of this partnership is crucial. This article explores the multifaceted landscape of India’s sustainable development journey, focusing on the significance of partnerships in achieving the SDGs.
“It is well known that we have followed the approach of “Sabka Saath, Sabka Vikas, Sabka Vishwas, Sabka Prayas” in our country… This is our guiding principle in global relations as well.” – PM Narendra MODI
Understanding Partnership for the Goals
Partnership for the Goals encapsulates a collaborative approach to addressing the 17 SDGs. In India, this involves concerted efforts to navigate the intricate web of socio-economic and environmental challenges. Key principles guiding these partnerships include inclusivity, transparency, and shared responsibility. The relevance of such partnerships in India is underscored by the need to harmonize diverse interests and mobilize resources efficiently.
India’s Journey towards Sustainable Development
India’s socio-economic and environmental landscape is a tapestry woven with complexities and opportunities. With a population exceeding 1.3 billion, the country faces challenges ranging from poverty and inequality to environmental degradation. However, the Indian government has exhibited a commitment to sustainable development through initiatives like the National Institution for Transforming India (NITI Aayog) and flagship programs like Swachh Bharat Abhiyan and Make in India. These efforts align with the SDGs, demonstrating a national resolve to tackle the interconnected challenges.
The Role of Stakeholders in Partnership
- Government Initiatives and Policies
India’s national development plans, such as the Five-Year Plans and Vision 2030, lay the groundwork for achieving the SDGs. The National Health Mission (NHM) and National Skill Development Mission (NSDM) exemplify targeted efforts to address health and education-related goals. Additionally, the Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY) aims to eradicate financial exclusion, contributing to poverty alleviation.
The NITI Aayog acts as a crucial institutional mechanism, coordinating efforts across ministries and engaging with stakeholders. Its comprehensive approach involves not only the integration of SDGs into policies but also the establishment of a monitoring framework to track progress.
Reference: NITI Aayog – Voluntary National Review Report 2022

- Private Sector Engagement
The private sector in India has become an instrumental partner in sustainable development. Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) initiatives mandated by the Companies Act, 2013, allocate resources for community development. Leading conglomerates like Tata Group and Reliance Industries actively contribute to education, healthcare, and environmental sustainability. Public-private partnerships, exemplified by initiatives like Smart Cities Mission, leverage private sector expertise for urban development.
Reference: Ministry of Corporate Affairs – CSR Report 2023
- Civil Society Participation
Non-Governmental Organizations (NGOs) play a pivotal role in grassroots engagement, addressing community-specific challenges. Organizations like SEWA (Self-Employed Women’s Association) empower women in the informal sector, aligning with SDG 5 (Gender Equality). Grassroots movements like Chipko and Narmada Bachao Andolan highlight the significance of community-led initiatives in environmental conservation.
Reference: Indian NGO Sector Report 2023
“If we want any significant development,
we must co-opt civil society.“
Global Collaborations and Diplomacy
India’s commitment to global collaboration is evident in its active participation in international forums, such as the United Nations and BRICS. Bilateral collaborations, such as the India-U.S. Climate and Clean Energy Agenda, exemplify efforts to align national priorities with global sustainability goals. India’s contributions to global SDG targets, particularly in areas like renewable energy and climate action, showcase its role as a responsible global stakeholder.
Challenges and Opportunities
While progress is evident, challenges persist. India faces obstacles such as uneven development, regional disparities, and environmental degradation. The need for infrastructure development often clashes with environmental concerns, requiring innovative solutions. However, these challenges present opportunities for sustainable innovation, inclusive development, and the harnessing of emerging technologies.
Case Studies
1. Clean India Mission (Swachh Bharat Abhiyan): A Paradigm for SDG 6 and SDG 11
The Swachh Bharat Abhiyan, launched in 2014, is a flagship initiative that exemplifies a successful partnership addressing SDG 6 (Clean Water and Sanitation) and SDG 11 (Sustainable Cities and Communities). At its core, the mission aimed to eliminate open defecation, improve solid waste management, and promote hygiene practices across the country.
Government Initiatives and Policies:
- The Government of India, through the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs, led the initiative by formulating policies and providing financial support to urban and rural local bodies.
- The construction of millions of toilets across the nation was a collaborative effort, involving government agencies, local authorities, and communities.
Private Sector Engagement:
- Private corporations actively participated through Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) initiatives, contributing funds and resources for toilet construction and maintenance.
- Partnerships with NGOs, such as Sulabh International, played a crucial role in implementing community-led sanitation programs.
Civil Society Participation:
- Grassroots engagement was pivotal, with communities actively participating in the construction and maintenance of toilets.
- Social and cultural influencers played a role in promoting the importance of sanitation and hygiene, leading to behavior change.
Reference: Swachh Bharat Abhiyan Impact Assessment Report 2023
The impact of the Swachh Bharat Abhiyan extends beyond the initial goals. The collaborative efforts resulted in a significant reduction in open defecation, improvements in sanitation infrastructure, and a decrease in waterborne diseases. The case study underscores the effectiveness of partnerships in achieving SDGs by addressing both environmental sustainability and public health.
2. Renewable Energy Initiatives: Advancing SDG 7
India’s ambitious targets for renewable energy, outlined in the National Solar Mission and National Wind Energy Mission, exemplify a successful partnership contributing to SDG 7 (Affordable and Clean Energy).
Government Initiatives and Policies:
- The Government of India, through the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy, formulated policies and set ambitious targets for the deployment of renewable energy sources.
- Incentives such as tax credits and subsidies were provided to encourage private sector participation in the renewable energy sector.
Private Sector Engagement:
- Private entities, including major corporations and independent power producers, actively invested in and developed renewable energy projects.
- Public-private partnerships facilitated the integration of renewable energy into the national grid, ensuring a sustainable and reliable energy supply.
International Collaboration:
- India collaborated with international organizations, such as the International Solar Alliance, to leverage global expertise and promote the adoption of solar energy.
- Technology transfer and knowledge-sharing agreements with countries like Germany and the United States accelerated the development of renewable energy infrastructure.
Reference: Ministry of New and Renewable Energy – Annual Report 2023
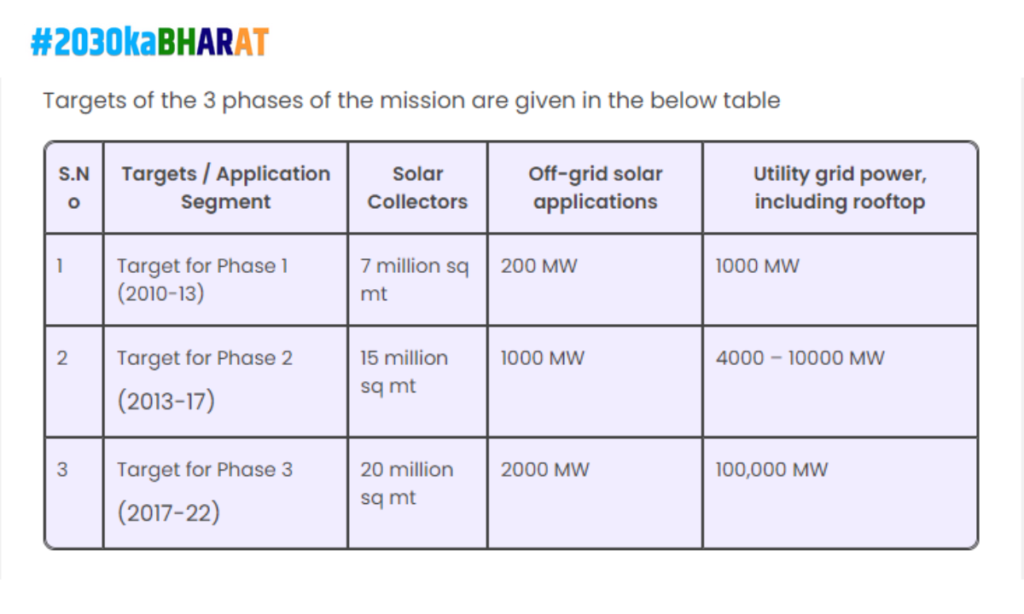
The impact of these initiatives is evident in the significant growth of renewable energy capacity in India. The country has become a global leader in solar energy deployment, contributing to a cleaner and more sustainable energy mix. The case study highlights how partnerships, spanning government, private sector, and international collaboration, can drive progress towards SDG 7 and address climate change challenges.
These case studies provide tangible examples of how partnerships for sustainable development are operationalized in India, showcasing the power of collaborative efforts in achieving specific SDGs.
Future Prospects
Looking ahead, India envisions sustainable development through a holistic approach. The incorporation of digital technologies, circular economy practices, and inclusive policies are anticipated. Emerging trends in public-private partnerships, impact investing, and social enterprises signal a dynamic future for sustainable development in India.
Conclusion
In conclusion, India’s journey towards sustainable development is intricately linked with the concept of “Partnership for the Goals.” Through collaborative efforts across government, private sector, and civil society, India navigates its unique challenges and contributes to global SDG targets. As the nation continues to evolve, fostering inclusive partnerships remains the linchpin for achieving a sustainable and equitable future. The lessons learned from India’s experience can serve as a blueprint for nations worldwide, emphasizing that true progress is achieved through collective action and shared responsibility.
